Sound for Interaction class 9
- Audio Effects Presentations
- Intro to digital theory
Digital Theory
Word of the Day Analog How stuff works - How Analog and Digital Recording Works
Analog vs. Digital the arguments in a nutshell
| Analog | Digital Good |
|---|---|
| Infinite dynamic quantization (infinite resolution) | Quantization error fix - more bit depth/oversampling |
| Good? - The warming effects 'we're used' to from tape compression. | Good?-'Perfect' reproduction of high frequencies - 'soundz harsh fix - 'using warm-sounding mikes and preamps (tubes)' |
| Bad - Tape noise and generation loss | Good - 'no generation loss' |
| Bad - 'Cheap recordings sound cheap' | Good - 'cheap recordings sound good but digital' |
* 'anything in quotes is what I like to call an opinion
Other Opinions
analog winner http://www.segall.com/atr.html
analog winner http://www.digido.com/analog_versus_digital.html
comparison http://www.outersound.com/osu/recording/
ana-dig.html Number Systems
| Hexadecimal Base 16 | Decimal Base 10 | Octal Base 8 | Binary Base 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0000 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0001 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 0010 |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 0011 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 0100 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 0101 |
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 0110 |
| 7 | 7 | 7 | 0111 |
| 8 | 8 | 10 | 1000 |
| 9 | 9 | 11 | 1001 |
| A | 10 | 12 | 1010 |
| B | 11 | 13 | 1011 |
| C | 12 | 14 | 1100 |
| D | 13 | 15 | 1101 |
| E | 14 | 16 | 1110 |
| F | 15 | 17 | 1111 |
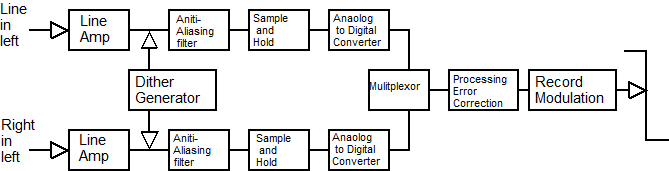
Sampling theory
sampling process [1]
Bit Depth
over 24 bit used mainly for internal processing and really high end audio equipment
24 bit Professional recording and internal processing
16 bit CD quality audio (not so good for processing)
8 bit Smaller size used for consumer voice stuff and multimedia
Sampling Rates
Some Common Sampling Rates
| Sampling Rate | Use |
|---|---|
| 192kHz | Professional recording and new fancy sound cards |
| 96kHz | Professional recording Modern Sound Cards HDDVD BlueRay SACD etc |
| 48 kHz | Professional recording (commonly used for TV/film) |
| 44.1 kHz | CD quality Audio |
| 22 kHz | Multimedia/ Games |
| 11 kHz | Multimedia/ Games |
File Size per Sampling rate and Bit Depth
| Sample Rate | Bit Width | File Size per minute |
| 96 kHz | 24-bit Stereo | 33.0 MB |
| 44.1 kHz | 16-bit Stereo | 10.5 MB |
| 44.1 kHz | 16-bit Mono | 5.3 MB |
| 44.1 kHz | 8-bit Stereo | 5.3 MB |
| 44.1 kHz | 8-bit Mono | 2.6 MB |
| 22 kHz | 16-bit Stereo | 5.3 MB |
| 22 kHz | 16-bit Mono | 2.6 MB |
| 22 kHz | 8-bit Stereo | 2.6 MB |
| 22 kHz | 8-bit Mono | 1.3 MB |
| 11 kHz | 16-bit Stereo | 2.6 MB |
| 11 kHz | 16-bit Mono | 1.3 MB |
| 11 kHz | 8-bit Stereo | 1.3 MB |
| 11 kHz | 8-bit Mono | 660 KB |
Note : Dropping the Sampling Rate or Bit Depth by half leads to half the file size
File formats
| name | ext. | info |
|---|---|---|
| aiff | .aif | audio interchange file format (mac native) supports markers and regions |
| sd2 | .sd2 | sound designer 2 (digidesign native) supports markers and regions |
| wave | .wav | wave file (Microsoft) many different formats most support markerz and regions |
| au-law | .au or .aul | au-law file (unix native) supports compression |
| RAM | .ram or .ra | Real audio File supports compression and streaming |
| Mpeg3 | .mp3 | Mpeg layer 3 supports variable compression and streaming (AMP) |
| AAC | .aac | Mpeg2 Advanced Audio Coding AC-3 standard NEW not supported yet http://www.execpc.com/%7Ereal/aac/index.html |
| MIDI | .mid | not and audio format |
| Modular (MOD) | .mod | kinda an audio format (used mainly for games) |
| ASF wmv | .asf .wmv | windows Media and Advanced Streaming Format Microsoft supports variable compression streaming video encryption |
CD Formats
- RedBook Audio standard CD audio format
- CDROM-XA (eXtended Archetecture) audio and data