Difference between revisions of "MTD2 class 11"
(→Digital Cameras) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Category:MTD2]] | |
| + | ==The Eye== | ||
| − | Helical Head recording Toshiba Firsts | + | The eyes resolution is much higher that that of a digital camera or video camera. |
| + | The human retina has about 6,000,000 color sensing cone cells and more than 100,000,000 rods that perceive light and dark. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The rod cells are sensitive enough to detect single particle of light (photon) and fire off an signal to the brain. As few as six of these single photon signals is enough for the brain to perceive a light flash. | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://photo.net/photo/edscott/vis00010.htm | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eyes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dynamic Range | ||
| + | :Light contrast of 100:1 or 1,000,000:1 over time | ||
| + | |||
| + | Color Vision | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_vision | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Digitizing Video== | ||
| + | |||
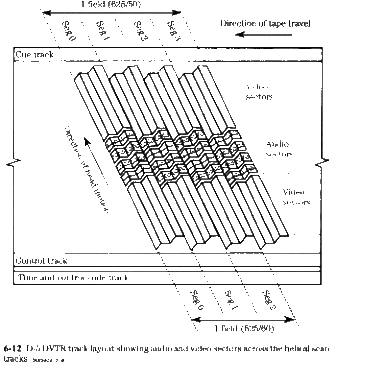
| + | [http://history.acusd.edu/gen/recording/magnetic4.html Helical Head recording Toshiba Firsts] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[IMAGE:Videotape1HelicalHead.gif]] | ||
| + | | [[IMAGE:Videotape2HelicalHead.gif]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
RGB Red Green Blue | RGB Red Green Blue | ||
| − | 8Bits each [3(RGB) *8(Bits) = 24 Bit color] or 2^24 = 16777216 colors Color Video uses YCC (YUV(PAL)/YIQ(NTSC)) to be | + | 8Bits each [3(RGB) *8(Bits) = 24 Bit color] or 2^24 = 16777216 colors Color Video uses [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YCbCr]YCC ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV YUV](PAL)/[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YIQ YIQ](NTSC)) to be compatible with Black and White Broadcast |
| − | Y is luminance (same | + | |
| + | Y is luminance (same luminance used in B&W broadcast). Luminance determines the brightness of the pixel | ||
The Two C's (the c's are known as chrominance) determine the hue. | The Two C's (the c's are known as chrominance) determine the hue. | ||
| − | Analog Video | + | ==Analog Video== |
| − | Composite | + | '''Composite''' |
| + | :One Cable. The luminance and color signals are merged onto one cable. Because of this merging some information is lost due to interference. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''S-Video (better)''' | ||
| + | :Separates the luminance and color signal onto separate cables that are encased in one cable | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Component (best)''' | ||
| + | :Each of of the YCC is given its own cable | ||
| − | + | {| align="center" border="1" | |
| − | S-Video | + | |- |
| + | |Tape Format ||Video Format || Quality || Applications | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |VHS ||Composite || Good || Home Video | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S-VHS, Hi-8 ||S-Video|| Better || pro-sumer, industrial video | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |BetaSP || Component || Best || broadcast | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Chroma Sub sampling http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroma_subsampling | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Because the human eye is less sensitive to color than to luminance, the chroma is often recorded with lower definition. 4:2:2 color http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4:2:2 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
4:1:1 color | 4:1:1 color | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Digital Cameras | + | Digital Video([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DV DV]) |
| + | :DV25 DVCAM, DVPRO DV50, DV100 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Digital Cameras== | ||
| − | Cameras | + | Cameras use a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) to convert light into electricty. [[http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/digital-camera2.htm How Digital Cameras Work]] |
A 3CCD camera splits the incoming light into three beam and uses three CCD's to capture each of the RGB values. | A 3CCD camera splits the incoming light into three beam and uses three CCD's to capture each of the RGB values. | ||
| − | A 1 CCD Camera can use a color filter array like the Bayer filter pattern to record the RGB color information. | + | A 1 CCD Camera can use a color filter array like the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayer_filter Bayer filter] pattern to record the RGB color information. |
| + | |||
Bayer filters have twice as many green pixels | Bayer filters have twice as many green pixels | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Homework | Homework | ||
| − | + | *Read Adobe [http://www.adobe.com/motion/primers.html DV Primer ] | |
| − | + | *Practice and demonstrate motion tweening and onion skin animations in two different flash files save as .swf | |
| + | *Animate on frame of you boards using motion tweening or onion skinning | ||
| + | |||
Links | Links | ||
| − | + | * [http://lipas.uwasa.fi/~f76998/video/conversion/ A Quick Guide to Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio Conversions] | |
| − | + | * [http://www.adobe.com/motion/primers.html Adobe DV Primer 2_6_02.aid] | |
| − | + | * [http://www.howstuffworks.com/camcorder.htm How Stuff Works Camcorder] | |
Latest revision as of 19:33, 11 April 2007
The Eye
The eyes resolution is much higher that that of a digital camera or video camera. The human retina has about 6,000,000 color sensing cone cells and more than 100,000,000 rods that perceive light and dark.
The rod cells are sensitive enough to detect single particle of light (photon) and fire off an signal to the brain. As few as six of these single photon signals is enough for the brain to perceive a light flash.
http://photo.net/photo/edscott/vis00010.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eyes
Dynamic Range
- Light contrast of 100:1 or 1,000,000:1 over time
Color Vision
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_vision
Digitizing Video
Helical Head recording Toshiba Firsts

|
|
RGB Red Green Blue
8Bits each [3(RGB) *8(Bits) = 24 Bit color] or 2^24 = 16777216 colors Color Video uses [1]YCC (YUV(PAL)/YIQ(NTSC)) to be compatible with Black and White Broadcast
Y is luminance (same luminance used in B&W broadcast). Luminance determines the brightness of the pixel The Two C's (the c's are known as chrominance) determine the hue.
Analog Video
Composite
- One Cable. The luminance and color signals are merged onto one cable. Because of this merging some information is lost due to interference.
S-Video (better)
- Separates the luminance and color signal onto separate cables that are encased in one cable
Component (best)
- Each of of the YCC is given its own cable
| Tape Format | Video Format | Quality | Applications |
| VHS | Composite | Good | Home Video |
| S-VHS, Hi-8 | S-Video | Better | pro-sumer, industrial video |
| BetaSP | Component | Best | broadcast |
Chroma Sub sampling http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroma_subsampling
Because the human eye is less sensitive to color than to luminance, the chroma is often recorded with lower definition. 4:2:2 color http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4:2:2 4:1:1 color
Digital Video(DV)
- DV25 DVCAM, DVPRO DV50, DV100
Digital Cameras
Cameras use a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) to convert light into electricty. [How Digital Cameras Work] A 3CCD camera splits the incoming light into three beam and uses three CCD's to capture each of the RGB values. A 1 CCD Camera can use a color filter array like the Bayer filter pattern to record the RGB color information.
Bayer filters have twice as many green pixels
Homework
- Read Adobe DV Primer
- Practice and demonstrate motion tweening and onion skin animations in two different flash files save as .swf
- Animate on frame of you boards using motion tweening or onion skinning
Links