Difference between revisions of "Sound for Interaction class 6"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Sound for Interaction]] | [[Category:Sound for Interaction]] | ||
| − | + | {{Template:Signal flow}} | |
| − | + | {{Template:Audio Levels}} | |
| + | {{Template:Audio connectors}} | ||
| + | {{Template:Microphones}} | ||
| − | + | {{Template:Audio Levels}} | |
| − | + | [[Template:Audio Levels]] | |
| + | ==Homework== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Sound for Interaction Voice Recording]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 04:24, 16 July 2007
Contents
Signal flow
Block Diagrams (how audio moves though a system)
todo
make examples of block diagram make diagram for room 605 make diagram for theater
Audio Levels
Good Level Audio Levels
- Microphone level - The level (or voltage) of signal generated by a microphone. Typically around 2 millivolts. Compare this with the two normal line levels
- Phono Level - little larger than mic level also has equalization based on standardized RIAA curve. use phono input a line
- Line Level - . There is an international standard for the level of inputs; it is around -10dBV(.316V) for semi-pro equipment, and about +4dBu(1.228V) for "pro" equipment. Line level outputs can come from tape decks, CD players, tuners, DAT decks, effects, etc. (1.228V:+4dBu and .316V:-10dBV)
- Speaker level - higher voltages for speakers
Audio Level Links
- Rane Pro Audio Reference dB
- Interactive Design Tools: Utilities : VRMS / dBm / dBu / dBV calculator
- http://www.the12volt.com/ohm/ohmslaw.asp
Audio connectors
- 1/8" (3.5mm) Connectors Jack Plug Connectors Tip ring sleeve
 mono
mono  stereo
stereo 
- 1/4"(6.35mm) Connectors


- Banana Plugs

- Binding Posts Bayonet Neill-Concelman/British Naval Connector type of signal varies or BNC

- RCA-Type video left audio right audio



- XLR Microphone XLR
- TOSLink http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TOSLINK

Bluffers guide to WIRES AND CONNECTORS
Transducers
Transducer = a device that converts one type of energy to another. A microphone converts acoustic energy to electrical energy. A speaker converts electrical energy to acoustical energy. They are both transducers.
Microphones
good reading Audio Technica Guide to Microphones
Types of microphones
- Dynamic
- Condenser
- Ribbon
- piezo electric (contact Mic)
other (Stereo, binaural, PZM- pressure zone microphone http://www.crownaudio.com/mics.htm)
Ribbon Mic
- The first type of mic was a Ribbn Microphone. Basically a light wieght ribbon that conducts electricity the is suspened in between two magnets. Older ribbon mics usally have a reduced frequency response.
http://www.coutant.org/ribbons.html
Dynamic Mics
- A light weight diaphragm is connected to a coil that is suspended between a magnet.
- A very light weight diaphragm is suspended in front of an electrically charged back plate. The two plates basically act as an open air capacitor. As the air pressure changed the distance between the plated the capacitance between the plates also changes.
Condenser microphones need Phantom Power to work.
Our stereo mic: Audio Technica AT825 [1]
Microphone Comparison
| Parameter | Dynamic | Condenser | Ribbon |
| Frequency Response | Good | Best | Worst |
| Dynamic Range | Good | Good | Worst |
| Durability | Best | Good | Worst |
Proximity Effect
The frequency response of a directional microphone changes as it it brought close to a source. The bass response increases.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_Effect#In_audio
http://www.csun.edu/~record/prox/prox.html
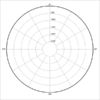
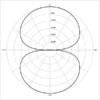
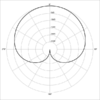
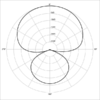
Polar Patterns
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microphones#Microphone_polar_patterns
- Omni-directional - all directions
- Bi-directional (figure 8)- front and back rejects on the side
- Uni-directional - one direction
- Cardioid - one direction with lobe
- Hypercardiod - really one direction with lobe
http://www.mikelights.com/micpolar.htmlALC Microphone Directionality Some pictures
http://www.csun.edu/~record/polar.html Some more Pictures
Stereo Mic Techniques
Spaced Omni's - two spaces Omni mics
XY - Coincident cardioids at 90 degrees
ORTF (Office de Radiodiffusion -- Television Francaise)110 degrees 17cm apart - Near Coincident Pair About.com Microphones Part 1
Dat Heads mic-FAQ.txt
Audio Levels
Good Level Audio Levels
- Microphone level - The level (or voltage) of signal generated by a microphone. Typically around 2 millivolts. Compare this with the two normal line levels
- Phono Level - little larger than mic level also has equalization based on standardized RIAA curve. use phono input a line
- Line Level - . There is an international standard for the level of inputs; it is around -10dBV(.316V) for semi-pro equipment, and about +4dBu(1.228V) for "pro" equipment. Line level outputs can come from tape decks, CD players, tuners, DAT decks, effects, etc. (1.228V:+4dBu and .316V:-10dBV)
- Speaker level - higher voltages for speakers
Audio Level Links
- Rane Pro Audio Reference dB
- Interactive Design Tools: Utilities : VRMS / dBm / dBu / dBV calculator
- http://www.the12volt.com/ohm/ohmslaw.asp