Difference between revisions of "OOP Class12"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Category:IAM Classes | + | [[Category:IAM Classes]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Interfaces Part2== | ==Interfaces Part2== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 10 June 2019
Contents
Interfaces Part2
There are many interfaces in the .net framework. Some that we have been working with are the [ICollection https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.collections.icollection(v=vs.110).aspx] [IList https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.collections.ilist(v=vs.110).aspx] and [IEnumerable https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.collections.ienumerable(v=vs.110).aspx]
These interfaces allow us to use methods in a List and Array.
Here is an example of sorting a list of ints or an int[]
int[] ints = new int[] { 5, 4, 2, 3, 1 };
foreach (var number in ints)
{
Console.Write(string.Format("{0}\t", number));
}
Console.WriteLine();
Array.Sort(ints); //Sort ints... they a primitive types so c# already knows how to sort them
foreach (var number in ints)
{
Console.Write(string.Format("{0}\t", number));
}
Console.WriteLine();
ints = ints.Reverse().ToArray();
foreach (var number in ints)
{
Console.Write(string.Format("{0}\t", number));
}
Console.WriteLine();
//mess it up again
ints = new int[] { 5, 4, 2, 3, 1 };
ints = ints.OrderBy(i => i).ToArray();
foreach (var number in ints)
{
Console.Write(string.Format("{0}\t", number));
}
Console.WriteLine();
//mess it up again
ints = new int[] { 5, 4, 2, 3, 1 };
//last way slightly uses agregate function to Order array by int, turns array into list so we can call foreach
ints.OrderBy(i => i).ToList().ForEach(ii=>Console.Write(string.Format("{0}\t", ii)));
Console.WriteLine();
Demo that we can do the same thing with lists with List
Some other ICollection Types that have more structure. These are known as Data Structures
//Colllection Types
List<int> ints = new List<int> { 5, 3, 4, 2, 1 };
Stack<int> intStack = new Stack<int>();
intStack.Push(1); //We push new item onto a stack
intStack.Push(2);
intStack.Push(3);
Console.WriteLine(intStack.Pop()); //We pop items off of a stack
Console.WriteLine(intStack.Pop());
Console.WriteLine(intStack.Pop());
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
intQueue.Enqueue(1);
intQueue.Enqueue(2);
intQueue.Enqueue(3);
Console.WriteLine(intQueue.Peek());
Console.WriteLine(intQueue.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(intQueue.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(intQueue.Dequeue());
Dictionary<string, string> States = new Dictionary<string, string>();
States.Add("AL", "Alabama");
States.Add("AK", "Alaska");
States.Add("AR", "Arizona");
foreach (var item in States)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} {1}", item.Key, item.Value));
}
SortedList<int, string> StatesSorted = new SortedList<int, string>();
StatesSorted.Add(1, "Delware");
StatesSorted.Add(2, "Pennsylvania");
StatesSorted.Add(3, "New Jersey");
foreach (var item in StatesSorted)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} {1}", item.Key, item.Value));
}
Console.ReadKey();
Now lets sort some dogs
class Dog : IComparable
{
public string Name;
protected int age;
public int Age { get { return age; } set { age = value; } }
public int Weight;
public string BarkSound;
public Dog()
{
this.Name = "fido";
this.BarkSound = "woof!";
this.Weight = 1;
}
public string About()
{
return string.Format("Hello my name is {0}. I'm {1} years old. I weigh {2} lbs", this.Name, this.Age, this.Weight);
}
public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
if (obj is Dog)
{
if (this.Age > ((Dog)obj).Age) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
and finally override some operators
public static int Compare(Dog left, Dog right)
{
if (object.ReferenceEquals(left, right))
{
return 0;
}
if (object.ReferenceEquals(left, null))
{
return -1;
}
return left.CompareTo(right);
}
public static bool operator <(Dog left, Dog right)
{
return (Compare(left, right) < 0);
}
public static bool operator >(Dog left, Dog right)
{
return (Compare(left, right) > 0);
}
Strategy Pattern
Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
http://www.dofactory.com/Patterns/PatternStrategy.aspx

Create Characters class and weapons class that uses the strategy pattern
http://iam.colum.edu/oop/classsource/ConsoleApplicationCharacters.zip
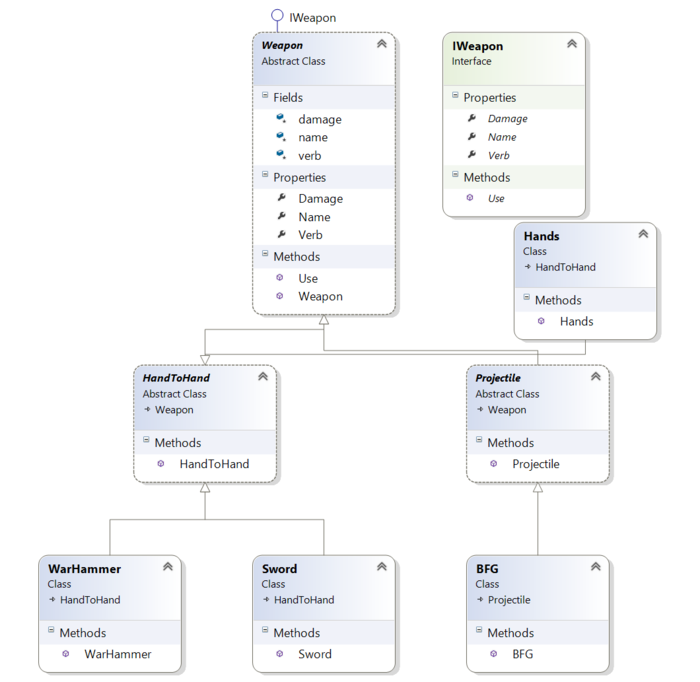
Weapons
public abstract class Weapon : IWeapon
{
protected string name, verb;
protected int damage;
public Weapon()
{
this.verb = "uses";
}
#region IWeapon Members
public string Name
{
get
{
return this.name;
}
set
{
this.name = value;
}
}
public string Verb
{
get
{
return this.verb;
}
set
{
this.verb = value;
}
}
public int Damage
{
get
{
return this.damage;
}
set
{
this.damage = value;
}
}
public string Use(Character c)
{
return c.TakeDamage(this.damage).ToString();
}
#endregion
}
|
public interface IWeapon
{
string Name
{
get;
set;
}
int Damage
{
get;
set;
}
string Verb { get; set; }
string Use(Character otherCharacter);
}
|
public abstract class HandToHand : Weapon
{
public HandToHand()
{
this.verb = "swings";
}
}
|
public class Hands : Characters.HandToHand
{
public Hands()
{
this.Name = "Hands";
this.verb = "punches";
this.damage = 1;
}
}
|
public class Sword : HandToHand
{
public Sword()
{
this.Name = "Sword";
this.Damage = 7;
}
}
|
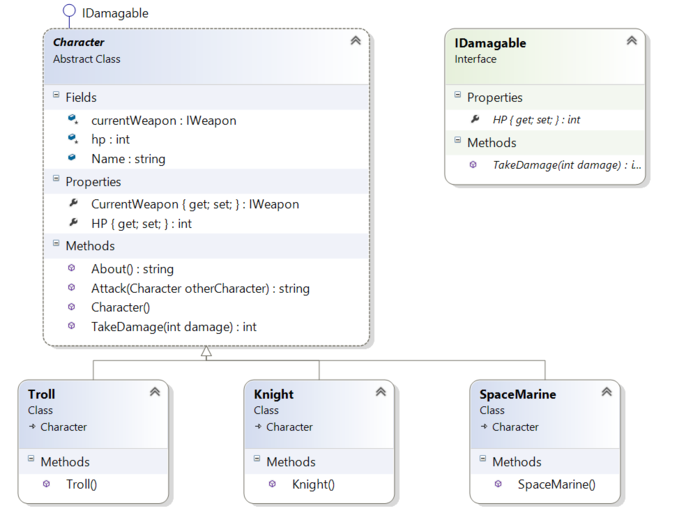
Characters
public abstract class Character : IDamagable
{
protected IWeapon currentWeapon;
protected int hp;
public string Name;
public Character()
{
this.Name = "Character";
this.hp = 100;
this.currentWeapon = new Hands();
}
public int HP
{
get
{
return this.hp;
}
set
{
this.hp = value;
}
}
public IWeapon CurrentWeapon
{
get
{
return this.currentWeapon;
}
set
{
this.currentWeapon = value;
}
}
public string About()
{
//TODO write about
return string.Format("About Character");
}
public string Attack(Character otherCharacter)
{
return string.Format("{0} {1} with {2} at {3} -{4} HP",
this.Name, currentWeapon.Verb, this.currentWeapon.Name,
otherCharacter.Name, this.currentWeapon.Use(otherCharacter));
}
public int TakeDamage(int damage)
{
this.hp -= damage;
return damage;
}
}
|
public interface IDamagable
{
int HP
{
get;
set;
}
int TakeDamage(int damage);
}
|
Than a specific character
public class Troll : Character
{
public Troll()
{
this.Name = "Troll";
this.currentWeapon = new WarHammer();
}
}
|
public class SpaceMarine : Character
{
public SpaceMarine()
{
this.Name = "Master Chief";
this.currentWeapon = new BFG();
}
}
|
public class Knight : Character
{
public Knight()
{
this.Name = "Sir Lancalot";
this.currentWeapon = new Sword();
}
}
|
Notice the IWeapon becomes a specific interchangeable weapon.
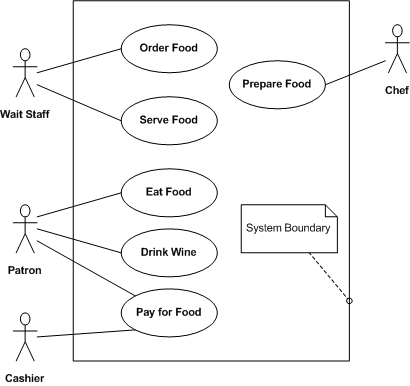
Use Case
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Use_case
Diagrams
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Use_case_diagram
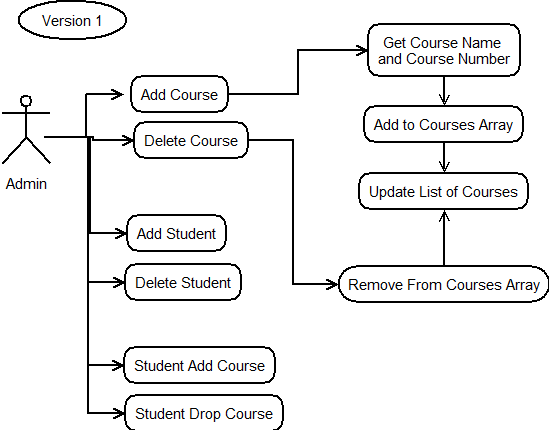
Windows Course App Use Case
Actors
- particiant outside of the system
Activity
- something an actor does
Version 1 breif use case
Actor Admin Course #Add a course to the system #Delete a course to the system Student #Add a student to the system #Delete a student to the system #Student add a course #Student remove a course
Use Cases often get translated in to sequence Diagrams
http://www.agilemodeling.com/artifacts/sequenceDiagram.htm
Home work
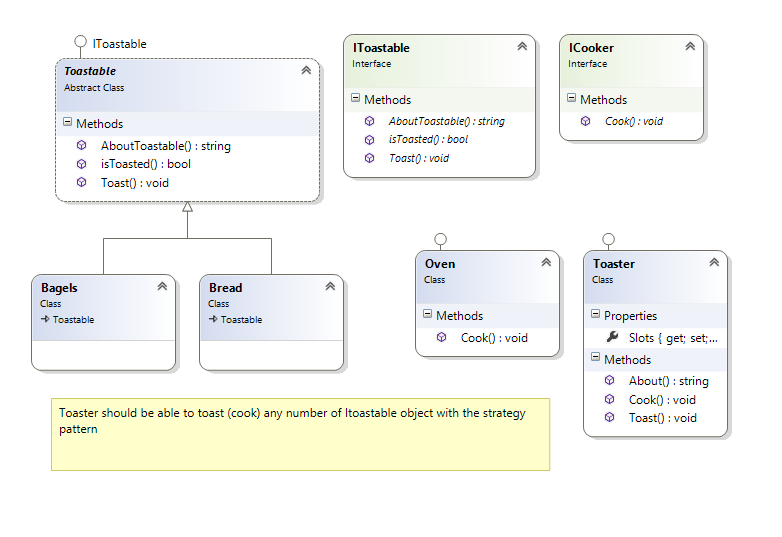
Toastable project in moodle : Toaster should be able to toast (cook) any number of Itoastable object with the strategy pattern
http://lms.colum.edu/mod/assign/view.php?id=161796
Make one of your classes sortable by implementing IComparable : Modify one of you classes to implements IComparable so that you objects may be sorted. Create an Array or LIst of you objects and demonstrate sorting them.