Difference between revisions of "MTD2 class 3"
(→Timbre/Harmonic structure) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:MTD2]] | [[Category:MTD2]] | ||
=Review Properties 1= | =Review Properties 1= | ||
| − | There is a good reading an a bunch of | + | There is a good reading an a bunch of supplemental reading in the [http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/sound/soundtoc.html High School Physics Tutorial] |
[[IMAGE:2SoundWaveCompared.png]] | [[IMAGE:2SoundWaveCompared.png]] | ||
Hold mouse over for answer | Hold mouse over for answer | ||
| − | #Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Lower | + | #Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Lower Frequency? |
#Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Higher Amplitude? | #Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Higher Amplitude? | ||
#Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Longer Wavelength? | #Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Longer Wavelength? | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Inner Ear | Inner Ear | ||
*Mallus, Incus, Stapes | *Mallus, Incus, Stapes | ||
| − | *Semi-Circular | + | *Semi-Circular Canals |
*Cochlea | *Cochlea | ||
*Estachian Tube | *Estachian Tube | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Perception of Amplitude and Frequency== | ==Perception of Amplitude and Frequency== | ||
| − | Humans do not hear all frequencies equally. We perceive different frequencies with equal energy to have different amplitudes. The Fletcher Munson Curves show the phons scale, how amplitude is | + | Humans do not hear all frequencies equally. We perceive different frequencies with equal energy to have different amplitudes. The Fletcher Munson Curves show the phons scale, how amplitude is perceived by frequency |
Fletcher Munson Curves 1 | Fletcher Munson Curves 1 | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
Adding two Simple Harmonic waves -Applet | Adding two Simple Harmonic waves -Applet | ||
| − | Adding two Simple | + | Adding two Simple Harmonic waves2 - Applet |
http://library.thinkquest.org/19537/java/Wave.html | http://library.thinkquest.org/19537/java/Wave.html | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
Different sound don't sound the same due to different fundamental frequencies, harmonics, complexity, and envelope. | Different sound don't sound the same due to different fundamental frequencies, harmonics, complexity, and envelope. | ||
| − | Timbre is made up of | + | Timbre is made up of Harmonics and Envelope. The Harmonics define the different frequencies present in a a sound and the envelope defines the amplitude through time. |
===Harmonic Structure=== | ===Harmonic Structure=== | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
Understanding Harmonics Fundamental Frequency and Harmonics | Understanding Harmonics Fundamental Frequency and Harmonics | ||
| − | + | Instruments | |
* Guitar string | * Guitar string | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
[http://www.harmony-central.com/Guitar/harmonics.html Understanding Harmonics] @ Harmony Central | [http://www.harmony-central.com/Guitar/harmonics.html Understanding Harmonics] @ Harmony Central | ||
| − | http://ptolemy.eecs.berkeley.edu/~eal/ | + | http://ptolemy.eecs.berkeley.edu/~eal/eecs20/berkeley/scale/demo/timbre.html |
| − | |||
| − | eecs20/berkeley/scale/demo/timbre.html | ||
==Envelope== | ==Envelope== | ||
| − | Envelope is the Time/Amplitude shape of the wave. It is | + | Envelope is the Time/Amplitude shape of the wave. It is essentially a means of amplitude thought time. |
Robert L Mott's Nine Components of Sound | Robert L Mott's Nine Components of Sound | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 15 January 2007
Contents
Review Properties 1
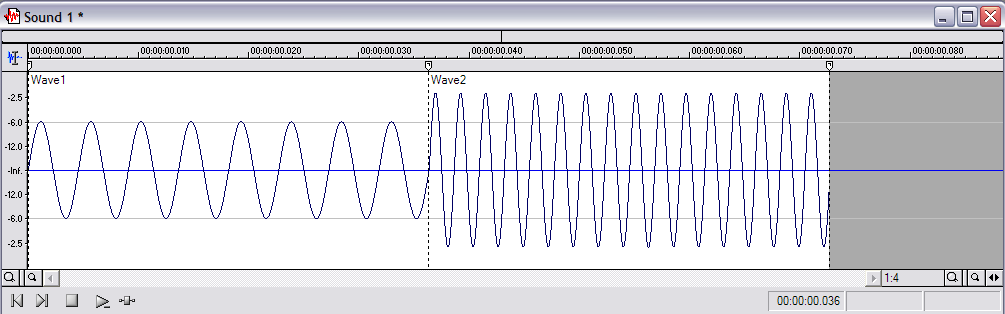
There is a good reading an a bunch of supplemental reading in the High School Physics Tutorial
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Lower Frequency?
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Higher Amplitude?
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Longer Wavelength?
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Faster Speed?
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) has a Higher Pitch?
- Which wave (Wave1 or Wave2) is Louder?
The Ear and Hearing Loss
Outer Ear
- Pinna
- Auditory Canal
- Ear Drum
Inner Ear
- Mallus, Incus, Stapes
- Semi-Circular Canals
- Cochlea
- Estachian Tube
- Auditory Canal
Hearing Loss
Perception of Amplitude and Frequency
Humans do not hear all frequencies equally. We perceive different frequencies with equal energy to have different amplitudes. The Fletcher Munson Curves show the phons scale, how amplitude is perceived by frequency
Fletcher Munson Curves 1 http://arts.ucsc.edu/EMS/Music/tech_background/TE-02/AcNumbers/AcNumbers.html
Fletcher Munson Curves 2 http://www.allchurchsound.com/ACS/edart/fmelc.html
Behaviour of sound waves
- Interference and Beats
- The Doppler Effect and Shock Waves
- Boundary Behavior
- Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction
Phase
Phase in measured in degrees.
The phase of a sound has to do with the time domain.
Adding two Simple Harmonic waves -Applet
Adding two Simple Harmonic waves2 - Applet
http://library.thinkquest.org/19537/java/Wave.html
In class demo of how waves add show beats
Timbre/Harmonic structure
Timbre is a descriptive word used to help describe the 'color' and envelope of a sound.
All sound is made up of simultaneous sounding tones. In the 1700 Joseph Fourier a French mathematical physicist proved that all sound can be synthesized be adding sine waves. The way these sine waves are added together make things sound different.
http://www.gac.edu/~huber/fourier/
Different sound don't sound the same due to different fundamental frequencies, harmonics, complexity, and envelope.
Timbre is made up of Harmonics and Envelope. The Harmonics define the different frequencies present in a a sound and the envelope defines the amplitude through time.
Harmonic Structure
http://www.rane.com/par-t.htm Harmonics defined @ rane
Understanding Harmonics Fundamental Frequency and Harmonics
Instruments
* Guitar string * Open-End Air Columns * Closed-End Air Columns
Natural harmonics are multiple of the fundamental/
Understanding Harmonics @ Harmony Central
http://ptolemy.eecs.berkeley.edu/~eal/eecs20/berkeley/scale/demo/timbre.html
Envelope
Envelope is the Time/Amplitude shape of the wave. It is essentially a means of amplitude thought time.
Robert L Mott's Nine Components of Sound
Attack -- Decay-- Sustain -- Release
Different Domains of sound
Time Domain
Time along X axis and Amplitude Y axis -Fixed 2/29/00
Sine wave looks like a sine wave
Frequency Domain
Freq. along X axis and Amplitude Along Y axis-Fixed 2/29/00
Sine wave looks like a line
RMS
root mean square Abbr. rms, RMS Mathematics. The square root of the average of the squares of a group of numbers. A useful and more meaningful way of averaging a group of numbers.
from http://www.rane.com/par-r.html
The RMS averaging method is a better method for determining the amplitude of sound. Dynamic Range Definition @http://www.rane.com/par-d.html
The dynamic range of an audio system or and audio performance is the difference between the peak noise level and the noise floor.
Dynamic Range
Dynamic range = (Peak Level - Noise Floor)
Head Room
Definition @http://www.rane.com/par-h.html
The head room of an audio system is is the difference between the nominal level and the Peak level (or clipping point) Frequency Response Definition @http://www.rane.com/par-f.html
The range in frequency that an audio system or program contains or can pass between certain deviation.
Home Work
- Study for Quiz on weeks 1,2, and 3 and Chapter 1 in Sound Design for Interactive Multimedia
- Sound Sculpture or Audio Enviroment
- Review for Quiz1 Next Week
Quiz 1 review
Properties of sound High school physics tutorial
* Sound Is a Longitudinal wave * Speed of sound (measured in m/s) * Frequency (measured in Hz) * Period (seconds per cycle) * Wavelength (measured in meters) * Amplitude/Pressure (for this class we will only look at dBs) * Phase (measured in degrees)
Understand the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves.
Be able to calculate frequency from wavelength or period and visa-versa.
Understand
* dB's * Different ways of representing and audio wave (the Domains of Sound) * Timbre/Harmonic structure * Dynamic Range and Headroom