Aggregation
Contents
Definition
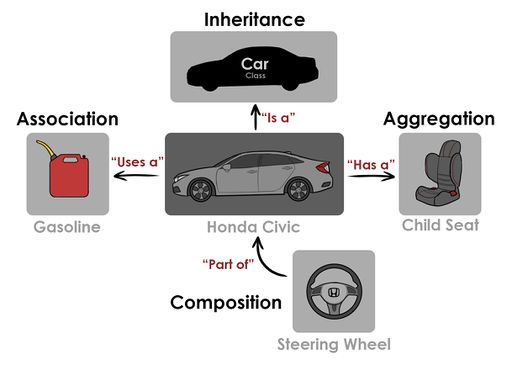
In object-oriented programming, aggregation is a whole/ part relationship between objects or classes. Class aggregation can correspond to physical containment in a model, such as a car that has an engine, doors, and windows. Class aggregation can also correspond to abstract containment such as a club and members. This relationship does not imply ownership, however.
Relevance
Explanation
Aggregation can be done by value or by reference. By value means that the two objects have the same lifespan and parts cannot be interchanged. By reference allows parts to be interchanged because the objects have been de-coupled. Another way to think of Aggregation is Object A “has an” Object B.
Composition is another form of aggregation, where the object is "part-of" another. This means, for the "part-of" object to exist, the other object also needs to exist. This is similar to a steering wheel or an engine to a car. If you were to get rid of the car, you would also get rid of the engine, steering wheel, and any other of its components. This is different to aggregation, which is similar to a car and a child's car seat, where if you get rid of the car, the child seat will continue to exist outside of the car.
Resources
https://atomicobject.com/resources/oo-programming/object-oriented-aggregation
https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/61376/aggregation-vs-composition