DD Class9
Second Normal Form
In order to reach 2NF the table must first be in 1NF
Second Normal Form eliminates functional dependencies on a partial key by putting the fields in a separate table from those that are dependent on the whole key.
'Remove Fields that are not dependent on the primary key'
Not Normal
Adresses
| CustNum | FirstName | LastName | Address | City | State | ZIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Doe | 12 Main Street | Sea Cliff | NY | 11579 |
| 2 | Alan | Johnson | 82 Evergreen Tr | Sea Cliff | NY | 11579 |
| 3 | Beth | Thompson | 1912 NE 1st St | Miami | FL | 33157 |
| 4 | Jacob | Smith | 142 Irish Way | South Bend | IN | 46637 |
| 5 | Sue | Ryan | 412 NE 1st St | Miami | FL | 33157 |
Normal
StatesZips
| ZIP | City | State |
|---|---|---|
| 11579 | Sea Cliff | NY |
| 33157 | Miami | FL |
| 46637 | South Bend | IN |
Address
| CustNum | FirstName | LastName | Address | ZIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Doe | 12 Main Street | 11579 |
| 2 | Alan | Johnson | 82 Evergreen Tr | 11579 |
| 3 | Beth | Thompson | 1912 NE 1st St | 33157 |
| 4 | Jacob | Smith | 142 Irish Way | 46637 |
| 5 | Sue | Ryan | 412 NE 1st St | 33157 |
In class
Normalize the books exmaple
Books
| Author | Title | Pages | Publisher | PublisherURL | Subject | ISBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michael Allen Dymmoch | The Man Who Understood Cats | 256 | Avon Books | http://www.harpercollins.com/imprints/index.aspx?imprintid=517994 | Fiction Mystery | 0380722658 |
| Joseph Cancellaro | Exploring Sound Design for Interactive Media | 272 | Thomson Delmar Learning | http://www.delmarlearning.com/ | Sound | 1401881025 |
Third Normal Form
Third Normal Form eliminates functional dependencies on non-key fields by putting them in a separate table. At this stage, all non-key fields are dependent on the key, the whole key and nothing but the key. Must be in second normal form.
Not normal
| Company | City | State | ZIP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acme Widgets | New York | NY | 10169 |
| ABC Corporation | Miami | FL | 33196 |
| XYZ, Inc. | Columbia | MD | 21046 |
Normal
| KompanyID | KompanyName | Zip |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acme Widgets | 10169 |
| 2 | ABC Corporation | 33196 |
| 3 | XYZ, Inc. | 21046 |
| Zip | CityID |
|---|---|
| 10169 | 1 |
| 33196 | 2 |
| 21046 | 3 |
| CityID | City |
|---|---|
| 1 | New York |
| 2 | Miami |
| 3 | Columbia |
| StateID | State |
|---|---|
| 1 | NY |
| 2 | FL |
| 3 | MD |
http://home.earthlink.net/~billkent/Doc/simple5.htm.
Many to Many Relationships
Look up tables. Are often used to define a many to many relation ship. These lookup tables often have a compound key.
See the Student Courses example from the Data Relationships page.
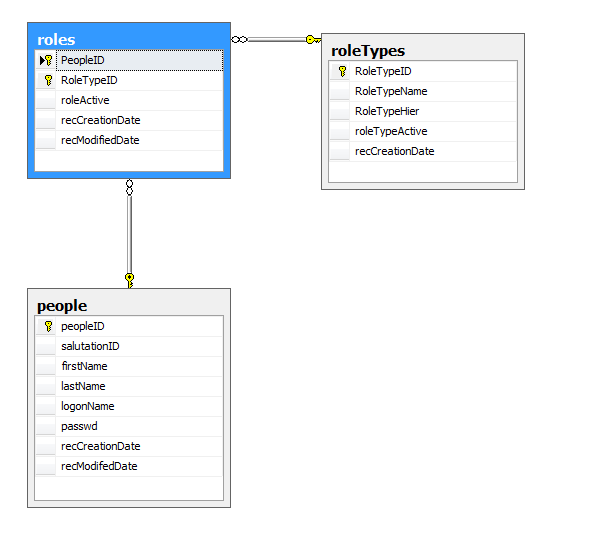
This is a demonstration of a logon system where users can have multiple roles. There is a compound key used on the roles table. The compound key consists of two or more foreign keys. Each combination of foreign keys must be unique.