Difference between revisions of "Bit"
esse quam videri
(→What does this mean) |
(→Explanation) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
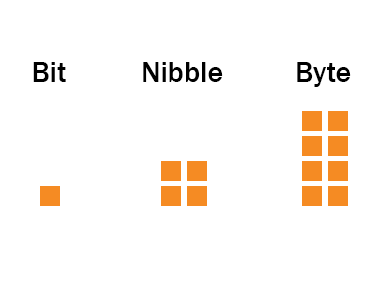
1 bit of data can only hold 0 or 1. 2 bits of data can hold 2^2 or 00, 01, 10 or 11. So, 8-bits of data can hold 256 patterns of binary digits (0 or 1). | 1 bit of data can only hold 0 or 1. 2 bits of data can hold 2^2 or 00, 01, 10 or 11. So, 8-bits of data can hold 256 patterns of binary digits (0 or 1). | ||
| − | [[File:Bit2.png | 650 px]] | + | [[File:Bit2.png | 650 px]] [[File:BitNibByte.png | 400px]] |
Credits: https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs101/bits-bytes.html | Credits: https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs101/bits-bytes.html | ||
Revision as of 18:16, 30 July 2019
Contents
Definition
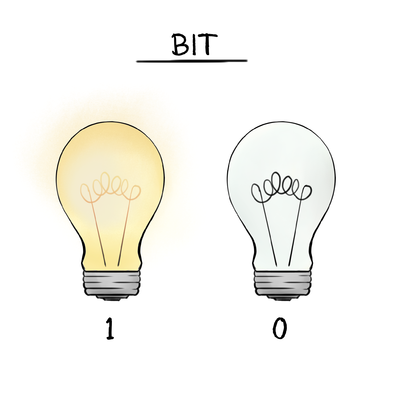
Also known as a Binary digIT, is the smallest in size and is either a 1 or a 0.
What does this mean
It's basically the smallest form of data storage you can think of. It is either present or absent, true or false, yes or no, 1 or 0.
Relevance
Explanation
Everything in a computer is 0's and 1's. The bit stores just a 0 or 1: it's the smallest building block of storage.
A bit is a computer storage reference, whereas Binary can refer to the number system as well. We mostly use Bit for Base 2 calculations. 1 bit of data can only hold 0 or 1. 2 bits of data can hold 2^2 or 00, 01, 10 or 11. So, 8-bits of data can hold 256 patterns of binary digits (0 or 1).
Credits: https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs101/bits-bytes.html